Basic Examples
This section presents some simple examples that show how to use μPanel with an Arduino UNO board.
1. LED Blink
In this example Arduino will create a simple panel with a LED and it will blink it at 1 Hz.
Hardware
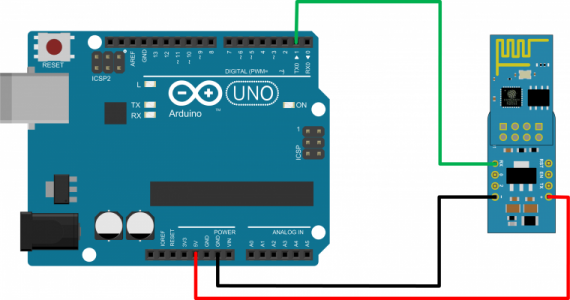
- Arduino UNO Board
- ESP-01 WiFi module (with µPanel Firmware)
- ADP-01 Breadboard adapter
- Breadboard wires (3 lines, Male-Female)
µPanel definition
Using the Online Panel Simulator you can easily design and check the panel layout before loading it on Arduino.
The panel definition is minimal, it contains only one LED with its label.
/L1G*15:0:Blinking;

Arduino Code
void setup() { // Initialize Serial Port Serial.begin(57600); // Let's uPanel start delay(3000); // Discharge old partial messages Serial.println(""); // Enable real-time response Serial.println("$PING 200"); // Send Panel (Single Green LED, 150% size on new line with text Blinking) Serial.println("$P:/L1G*15:0:Blinking;"); } void loop() { delay(500); // Wait 0.5 s Serial.println("#L11"); // Turn ON LED 1 delay(500); // Wait 0.5 s Serial.println("#L10"); // Turn OFF LED 1 }
2. One-digit chronometer
In this example a simple chronometer is implemented using one 7-segment LCD. Arduino will increment a variable at 1 Hz rate and will update the display state accordingly.
Hardware
Hardware and connections are the same as in the previous example:
- Arduino UNO Board
- ESP-01 WiFi module (with µPanel Firmware)
- ADP-01 Breadboard adapter
- Breadboard wires (3 lines)
µPanel definition
The panel definition is very simple and quite similar to the first one presented in Design Examples, just an additional text has been added in order to display the example reference.
D!228;*10/T*15:μPanel-Arduino Example 2;{%100,3!88F,228}/20{-3r30p20!228,114*15{T:Run;|L1G:0;_T:Stop;|L2R:0;}|{^*8L35:0;_T:Counter;}}
Arduino Code
void setup() { // Initialize Serial Port Serial.begin(57600); // Let's uPanel start delay(3000); // Discharge old partial messages Serial.println(""); // Send Panel Serial.print("$P:D!228;*10/T*15:μ-Arduino Example 2;{%100,3!88F,228}/20"); Serial.println("{-3r30p20!228,114*15{T:Run;|L1G:0;_T:Stop;|L2R:0;}|{^*8L35:0;_T:Counter;}}"); // Turn ON LED 1 Serial.println("#L11"); } long int n = 0; // Define and initialise counter void loop() { // Wait 1 s delay(1000); // Set LED 3 State and increment counter Serial.print("#L3"); Serial.println((n++ % 10),DEC); }
3. Switch a LED On/Off
In this example a switch and a LED will be placed on the Panel. Arduino will be waiting for the user to change the switch state and will update the LED status accordingly. This is the first example where Arduino has to receive messages sent by the Panel, thus, we have to connect the Arduino Rx line and include into the Arduino code the functions to read the incoming messages.
Hardware
- Arduino UNO Board
- ESP-01 WiFi module (with µPanel Firmware)
- ADP-01 Breadboard adapter
- Breadboard wires (4 lines)
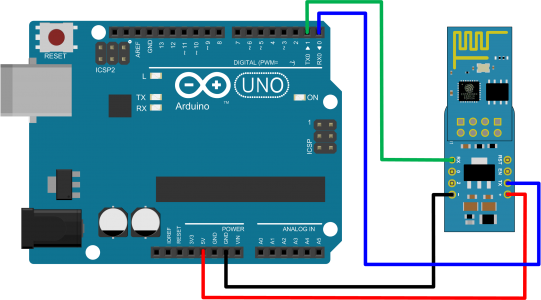
Please note that for programming Arduino Uno, the RxD line (blue wire) has to be disconnected from the WiFi Module
µPanel definition
The panel definition includes a text for the panel title, a standard green LED and a On/Off switch of type 2.
D!228;T*15:μPanel-Arduino Example 3;{%100,3!88F,228}*20/L1G:0:LED;*10/W1:0;

Arduino Code
void setup() { // Initialize Serial Port Serial.begin(57600); // Let uPanel to start delay(3000); // Discharge old partial messages and activate real-time response Serial.println("\n$PING 200"); // Send Panel (A LED and a Switch) Serial.println("$P:D!228;T*15:μ-Arduino Example 3;{%100,3!88F,228}*20/L1G:0:LED;*10/W1:0;"); } String Msg; void loop() { int c; while ((c = Serial.read()) > '\n') Msg += (char) c; // Read incoming chars, if any, until new line if (c == '\n') // is the message complete? { if (Msg.equals("#W10")) Serial.println("#L10"); // Turn OFF LED 1 if switch is OFF if (Msg.equals("#W11")) Serial.println("#L11"); // Turn ON LED 1 if switch is ON Msg = ""; } }
4. Push Counter
In this example a push button will be placed on the Panel. Arduino will count how many times the user pushes the button. The counter value will be shown on the Panel above the button.
Hardware
Hardware and connections are the same as in the previous example:
- Arduino UNO Board
- ESP-01 WiFi module (with µPanel Firmware)
- ADP-01 Breadboard adapter
- Breadboard wires (4)
µPanel definition
The panel definition includes a text for the panel title, a Message to display the counter value and a push Button.
D!228;T*15:μPanel-Arduino Example 4;{%100,3!88F,228}*20/T:Counter:;&M1:0;//B1p20r40:INCREMENT;

Arduino Code
void setup() { // Initialize Serial Port Serial.begin(57600); // Let uPanel to start delay(3000); // Discharge old partial messages and activate real-time response Serial.println("\n$PING 200"); // Send Panel (a Message and a Button) Serial.println("$P:D!228;T*15:μ-Arduino Example 4;{%100,3!88F,228}*20/T:Counter:;&M1:0;//B1p20r40:INCREMENT;"); } String Msg; int n = 0; // Create the counter variable void loop() { int c; while ((c = Serial.read()) > '\n') Msg += (char) c; // Read incoming chars, if any, until new line if (c == '\n') // is message complete? { if (Msg.equals("#B1P")) // has Button 1 been pushed? { Serial.print("#M1"); // Update message 1 text: Serial.println(++n,DEC); // increment and send the counter value } Msg = ""; } }

