Esempi intermedi
Questa sezione presenta alcuni esempi di media complessità che mostrano come utilizzare μPanel con una scheda Arduino UNO.
1. Utilizzo degli slider
In questo esempio Arduino leggerà in tempo reale la posizione di un cursore sul pannello e aggiorna una barra analogica conseguenza con 20 Hz di tempo rinfrescante.
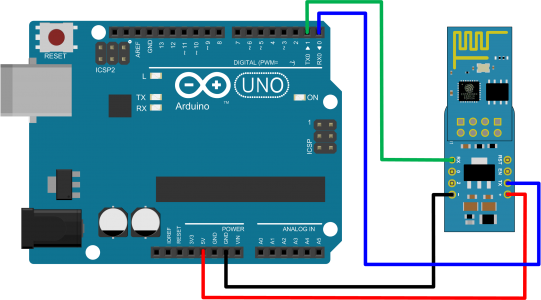
Hardware
- Arduino UNO
- Modulo ESP-01 WiFi (con µPanel Firmware)
- Adattatore per Breadboard ADP-01
- Breadboard wires (4)
Definizione μPanel
La definizione del pannello contiene il titolo del pannello, una barra analogica personalizzata e un cursore. L’intervallo di notifica cursore è impostato a 50 ms (20 Hz).
D!228;T*15:μPanel-Arduino Example Slider 1;{%100,3!88F,228}//A1%90-3:0:50:100:!F00;/30R1%90:0:100:1:50:50;

Arduino Code
void setup() { Serial.begin(57600); // Initialise serial delay(3000); // Let's the module start // Send Panel discharging old partial messages Serial.println("\n$P:D!228;T*15:μ-Arduino Example 1;{%100,3!88F,228}//A1%90-3:0:50:100:!F00;/30R1%90:0:100:1:50:50;"); } String Msg; void loop() { int c; while ((c = Serial.read()) > '\n') Msg += (char) c; // Read incoming chars, if any, until new line if (c == '\n') // is message complete? { Msg.toUpperCase(); // Catch partial slider positions too if (Msg.substring(0,4).equals("#R1:")) // has the slider been moved? { Serial.print("#A1:"); // Update the Analog bar Serial.println(Msg.substring(4)); // with the Slider value } Msg = ""; } }
2. Uso degli slider (2)
In questo esempio Arduino leggerà in tempo reale la posizione di un cursore sul pannello e aggiornerà sia una barra analogico e un display base 7 segmenti, con 20 Hz di tempo rinfrescante.
Hardware
- Arduino UNO
- Modulo ESP-01 WiFi (con µPanel Firmware)
- Adattatore per breadboard ADP-01
- Cavi Breadboard (4)

Definizione μPanel
La definizione pannello contiene il titolo del pannello, un analogo bar personalizzato e un cursore. L’intervallo di notifica cursore è impostato a 50 ms (20 Hz).
D!228;T*15:μPanel-Arduino Example 5;{%100,3!88F,228}//L15:0;L25:0;//A1%90-3:0:50:100:!F00;/30R1%90:0:100:1:50:50;

Arduino Code
void setup() { Serial.begin(57600); // Initialise serial delay(3000); // Let's the module start // Send Panel discharging old partial messages Serial.print("\n$P:D!228;T*15:μ-Arduino Slider 2;{%100,3!88F,228}"); Serial.println("//L15:5;L25:0;//A1%90-3:0:50:100:!F00;/30R1%90:0:100:1:50:50;"); } String Msg; void loop() { int c; while ((c = Serial.read()) > '\n') Msg += (char) c; // Read incoming chars, if any, until new line if (c == '\n') // is message complete? { Msg.toUpperCase(); // Catch partial slider positions too if (Msg.substring(0,4).equals("#R1:")) // has the slider been moved? { Serial.print("#A1:"); // Update the Analog bar Serial.println(Msg.substring(4)); // with the Slider value int v = (int) Msg.substring(4).toInt(); // Read the Slider position int d1 = (v / 10) % 10; // Compute the first LCD digit int d2 = v % 10; // Compute the second LCD digit Serial.print("#L1"); Serial.println(d1,DEC); // Update the first LCD digit Serial.print("#L2"); Serial.println(d2,DEC); // Update the second LCD digit } Msg = ""; } }

